A Fully-Automated Approach to Segmentation and Registration of SPECT/CT Data for Pulmonary Diagnosis
Members:
|
|
|
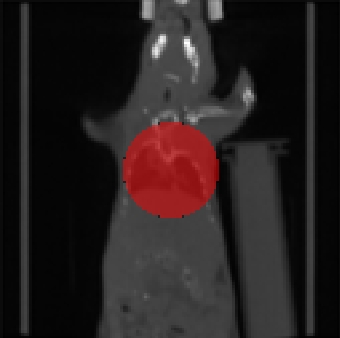
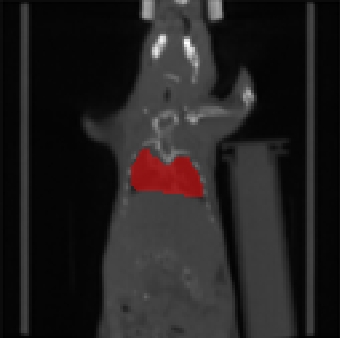
| Fig. 1: Automatically generated starting configuration (left) refined using a modified Chan-Vese approach (right). | |
|

|
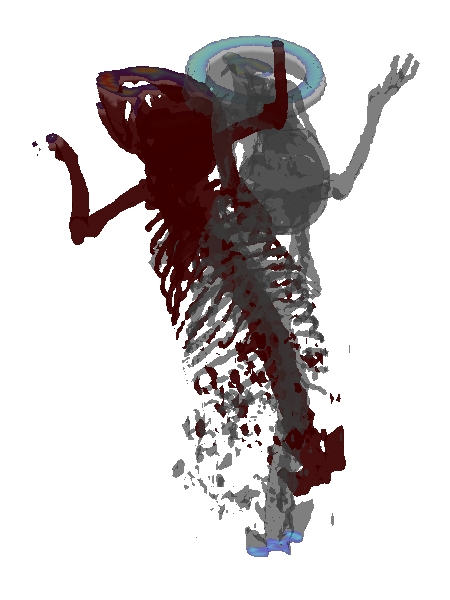
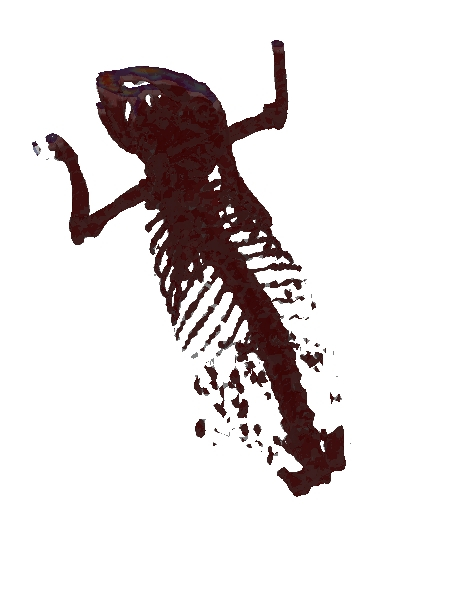
| Fig. 2: Hard tissue based visualization of fused 3D data before (left) and after (right) alignment. | |
Overview:
In the recent past nuclear imaging has influenced areas such as drug design and development. The amount of image data to be analyzed is typically huge, as temporal and spatial developments need to be resolved. Automated and unsupervised analysis tools are inevitable to keep time and cost requirements reasonable.
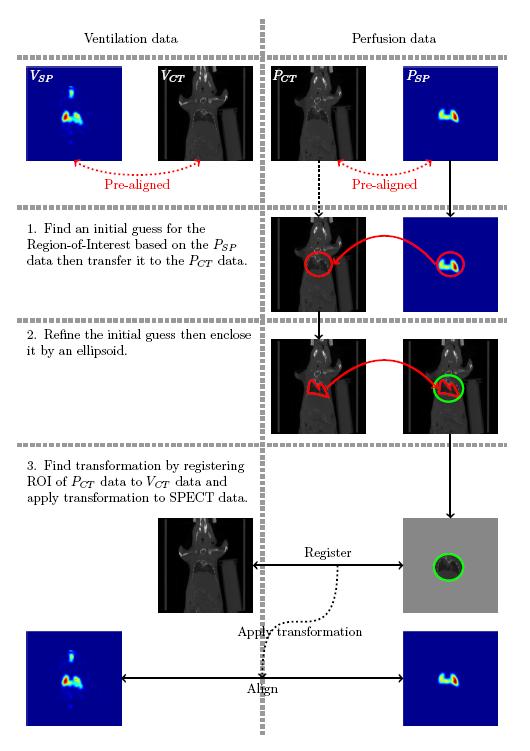
Ventilation and perfusion SPECTs show large structural differences since both modalities show the diffusion of a contrast agent through the lungs in different mediums. To supply missing structural information, pairs of combined SPECT CT ventilation and perfusion data are acquired.
An alignment of the ventilation and perfusion SPECT data is achieved by using an alignment strategy for the surrogate CT data, where the key challenge is the automated identification of the target region. Here, we used a modification of the Chan-Vese segmentation method.